
2023 AMC10/12A解析更难?or 更简单?
我们先来看一下2023年最新的真题:





2023 AMC 10A Answer Key
- E
- A
- A
- D
- E
- D
- B
- D
- E
- D
- C
- B
- C
- B
- E
- B
- A
- D
- E
- D
- D
- D
- C
- C
- A
Problem 1
Cities ![]() and
and ![]() are
are ![]() miles apart. Alicia lives in
miles apart. Alicia lives in ![]() and Beth lives in
and Beth lives in ![]() . Alicia bikes towards
. Alicia bikes towards ![]() at 18 miles per hour. Leaving at the same time, Beth bikes toward
at 18 miles per hour. Leaving at the same time, Beth bikes toward ![]() at 12 miles per hour. How many miles from City
at 12 miles per hour. How many miles from City ![]() will they be when they meet?
will they be when they meet?

Problem 2
The weight of ![]() of a large pizza together with
of a large pizza together with ![]() cups of orange slices is the same weight of
cups of orange slices is the same weight of ![]() of a large pizza together with
of a large pizza together with ![]() cups of orange slices. A cup of orange slices weigh
cups of orange slices. A cup of orange slices weigh ![]() of a pound. What is the weight, in pounds, of a large pizza?
of a pound. What is the weight, in pounds, of a large pizza?

Problem 3
How many positive perfect squares less than ![]() are divisible by
are divisible by ![]() ?
?

Problem 4
A quadrilateral has all integer side lengths, a perimeter of ![]() , and one side of length
, and one side of length ![]() . What is the greatest possible length of one side of this quadrilateral?
. What is the greatest possible length of one side of this quadrilateral?

Problem 5
How many digits are in the base-ten representation of ![]() ?
?

Problem 6
An integer is assigned to each vertex of a cube. The value of an edge is defined to be the sum of the values of the two vertices it touches, and the value of a face is defined to be the sum of the values of the four edges surrounding it. The value of the cube is defined as the sum of the values of its six faces. Suppose the sum of the integers assigned to the vertices is ![]() . What is the value of the cube?
. What is the value of the cube?

Problem 7
Janet rolls a standard 6-sided die 4 times and keeps a running total of the numbers she rolls. What is the probability that at some point, her running total will equal 3?

Problem 8
Barb the baker has developed a new temperature scale for her bakery called the Breadus scale, which is a linear function of the Fahrenheit scale. Bread rises at ![]() degrees Fahrenheit, which is
degrees Fahrenheit, which is ![]() degrees on the Breadus scale. Bread is baked at
degrees on the Breadus scale. Bread is baked at ![]() degrees Fahrenheit, which is
degrees Fahrenheit, which is ![]() degrees on the Breadus scale. Bread is done when its internal temperature is
degrees on the Breadus scale. Bread is done when its internal temperature is ![]() degrees Fahrenheit. What is this, in degrees, on the Breadus scale?
degrees Fahrenheit. What is this, in degrees, on the Breadus scale?

Problem 9
A digital display shows the current date as an ![]() -digit integer consisting of a
-digit integer consisting of a ![]() -digit year, followed by a
-digit year, followed by a ![]() -digit month, followed by a
-digit month, followed by a ![]() -digit date within the month. For example, Arbor Day this year is displayed as 20230428. For how many dates in
-digit date within the month. For example, Arbor Day this year is displayed as 20230428. For how many dates in ![]() does each digit appear an even number of times in the 8-digital display for that date?
does each digit appear an even number of times in the 8-digital display for that date?

Problem 10
Maureen is keeping track of the mean of her quiz scores this semester. If Maureen scores an ![]() on the next quiz, her mean will increase by
on the next quiz, her mean will increase by ![]() . If she scores an
. If she scores an ![]() on each of the next three quizzes, her mean will increase by
on each of the next three quizzes, her mean will increase by ![]() . What is the mean of her quiz scores currently?
. What is the mean of her quiz scores currently?

Problem 11
A square of area ![]() is inscribed in a square of area
is inscribed in a square of area ![]() , creating four congruent triangles, as shown below. What is the ratio of the shorter leg to the longer leg in the shaded right triangle?
, creating four congruent triangles, as shown below. What is the ratio of the shorter leg to the longer leg in the shaded right triangle?![[asy] size(200); defaultpen(linewidth(0.6pt)+fontsize(10pt)); real y = sqrt(3); pair A,B,C,D,E,F,G,H; A = (0,0); B = (0,y); C = (y,y); D = (y,0); E = ((y + 1)/2,y); F = (y, (y - 1)/2); G = ((y - 1)/2, 0); H = (0,(y + 1)/2); fill(H--B--E--cycle, gray); draw(A--B--C--D--cycle); draw(E--F--G--H--cycle); [/asy]](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/7/6/3/763eea423cc19d0e0a602d3e907bd5edc03cc6b7.png)

Problem 12
How many three-digit positive integers ![]() satisfy the following properties?
satisfy the following properties?
The number ![]() is divisible by
is divisible by ![]() . The number formed by reversing the digits of
. The number formed by reversing the digits of ![]() is divisible by
is divisible by ![]() .
.

Problem 13
Abdul and Chiang are standing ![]() feet apart in a field. Bharat is standing in the same field as far from Abdul as possible so that the angle formed by his lines of sight to Abdul and Chiang measures
feet apart in a field. Bharat is standing in the same field as far from Abdul as possible so that the angle formed by his lines of sight to Abdul and Chiang measures ![]() . What is the square of the distance (in feet) between Abdul and Bharat?
. What is the square of the distance (in feet) between Abdul and Bharat?

Problem 14
A number is chosen at random from among the first ![]() positive integers, and a positive integer divisor of that number is then chosen at random. What is the probability that the chosen divisor is divisible by
positive integers, and a positive integer divisor of that number is then chosen at random. What is the probability that the chosen divisor is divisible by ![]() ?
?

Problem 15
An even number of circles are nested, starting with a radius of ![]() and increasing by
and increasing by ![]() each time, all sharing a common point. The region between every other circle is shaded, starting with the region inside the circle of radius
each time, all sharing a common point. The region between every other circle is shaded, starting with the region inside the circle of radius ![]() but outside the circle of radius
but outside the circle of radius ![]() An example showing
An example showing ![]() circles is displayed below. What is the least number of circles needed to make the total shaded area at least
circles is displayed below. What is the least number of circles needed to make the total shaded area at least ![]() ?
?
![[asy] filldraw(circle((0,0),8),gray); filldraw(circle((-1,0),7),white); filldraw(circle((-2,0),6),gray); filldraw(circle((-3,0),5),white); filldraw(circle((-4,0),4),gray); filldraw(circle((-5,0),3),white); filldraw(circle((-6,0),2),gray); filldraw(circle((-7,0),1),white); [/asy]](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/a/a/3/aa3c94ca7814105299a9086afbfcb5b4ecaf2609.png)

Problem 16
In a table tennis tournament every participant played every other participant exactly once. Although there were twice as many right-handed players as left-handed players, the number of games won by left-handed players was ![]() more than the number of games won by right-handed players. (There were no ties and no ambidextrous players.) What is the total number of games played?
more than the number of games won by right-handed players. (There were no ties and no ambidextrous players.) What is the total number of games played?

Problem 17
Let ![]() be a rectangle with
be a rectangle with ![]() and
and ![]() . Point
. Point ![]() and
and ![]() lie on
lie on ![]() and
and ![]() respectively so that all sides of
respectively so that all sides of ![]() and
and ![]() have integer lengths. What is the perimeter of
have integer lengths. What is the perimeter of ![]() ?
?

Problem 18
A rhombic dodecahedron is a solid with ![]() congruent rhombus faces. At every vertex,
congruent rhombus faces. At every vertex, ![]() or
or ![]() edges meet, depending on the vertex. How many vertices have exactly
edges meet, depending on the vertex. How many vertices have exactly ![]() edges meet?
edges meet?

Problem 19
The line segment formed by ![]() and
and ![]() is rotated to the line segment formed by
is rotated to the line segment formed by ![]() and
and ![]() about the point
about the point ![]() . What is
. What is ![]() ?
?

Problem 20
Each square in a ![]() grid of squares is colored red, white, blue, or green so that every
grid of squares is colored red, white, blue, or green so that every ![]() square contains one square of each color. One such coloring is shown on the right below. How many different colorings are possible?
square contains one square of each color. One such coloring is shown on the right below. How many different colorings are possible?
![[asy] unitsize(0.5cm, 0.5cm); draw((0,0)--(9,0)--(9,9)--(0,9)--cycle); draw((0,3)--(9,3)); draw((0,6)--(9,6)); draw((3,0)--(3,9)); draw((6,0)--(6,9)); draw((18,0)--(27,0)--(27,9)--(18,9)--cycle); draw((18,3)--(27,3)); draw((18,6)--(27,6)); draw((21,0)--(21,9)); draw((24,0)--(24,9)); label("R", (19.5,1.5)); label("B", (22.5,1.5)); label("R", (25.5,1.5)); label("G", (19.5,4.5)); label("W", (22.5,4.5)); label("G", (25.5,4.5)); label("B", (19.5,7.5)); label("R", (22.5,7.5)); label("B", (25.5,7.5)); [/asy]](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/3/9/6/3968daf0b2ac62e635c0eee9dda627be9e15fe30.png)

Problem 21
Let ![]() be the unique polynomial of minimal degree with the following properties:
be the unique polynomial of minimal degree with the following properties:
 has a leading coefficient
has a leading coefficient  ,
, is a root of
is a root of  ,
, is a root of
is a root of  ,
, is a root of
is a root of  , and
, and is a root of
is a root of  .
.
The roots of ![]() are integers, with one exception. The root that is not an integer can be written as
are integers, with one exception. The root that is not an integer can be written as ![]() , where
, where ![]() and
and ![]() are relatively prime integers. What is
are relatively prime integers. What is ![]() ?
?

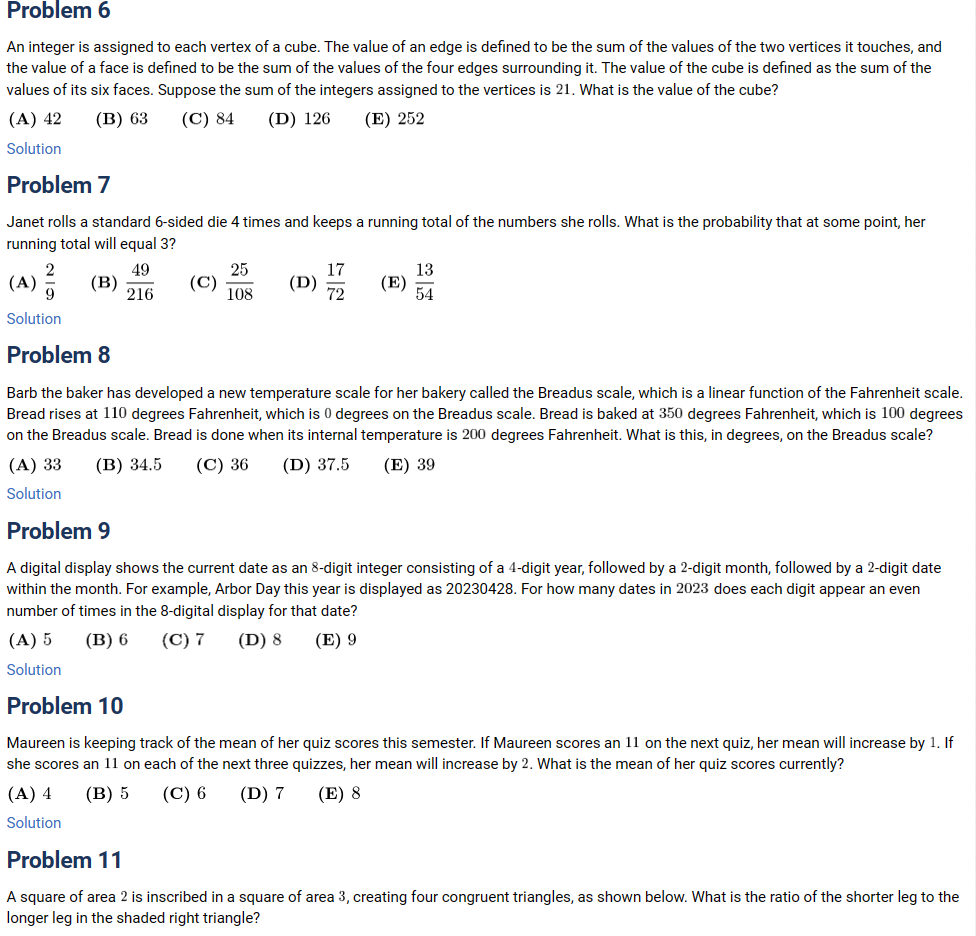
Problem 22
Circle ![]() and
and ![]() each have radius
each have radius ![]() , and the distance between their centers is
, and the distance between their centers is ![]() . Circle
. Circle ![]() is the largest circle internally tangent to both
is the largest circle internally tangent to both ![]() and
and ![]() . Circle
. Circle ![]() is internally tangent to both
is internally tangent to both ![]() and
and ![]() and externally tangent to
and externally tangent to ![]() . What is the radius of
. What is the radius of ![]() ?
?
![[asy] import olympiad; size(10cm); draw(circle((0,0),0.75)); draw(circle((-0.25,0),1)); draw(circle((0.25,0),1)); draw(circle((0,6/7),3/28)); pair A = (0,0), B = (-0.25,0), C = (0.25,0), D = (0,6/7), E = (-0.95710678118, 0.70710678118), F = (0.95710678118, -0.70710678118); dot(B^^C); draw(B--E, dashed); draw(C--F, dashed); draw(B--C); label("$C_4$", D); label("$C_1$", (-1.375, 0)); label("$C_2$", (1.375,0)); label("$\frac{1}{2}$", (0, -.125)); label("$C_3$", (-0.4, -0.4)); label("$1$", (-.85, 0.70)); label("$1$", (.85, -.7)); import olympiad; markscalefactor=0.005; [/asy]](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/4/0/6/406135ba18fccc6f68ffce10d698ac01c265ec90.png)

Problem 23
If the positive integer ![]() has positive integer divisors
has positive integer divisors ![]() and
and ![]() with
with ![]() , then
, then ![]() and
and ![]() are said to be
are said to be ![]() divisors of
divisors of ![]() . Suppose that
. Suppose that ![]() is a positive integer that has one complementary pair of divisors that differ by
is a positive integer that has one complementary pair of divisors that differ by ![]() and another pair of complementary divisors that differ by
and another pair of complementary divisors that differ by ![]() . What is the sum of the digits of
. What is the sum of the digits of ![]() ?
?

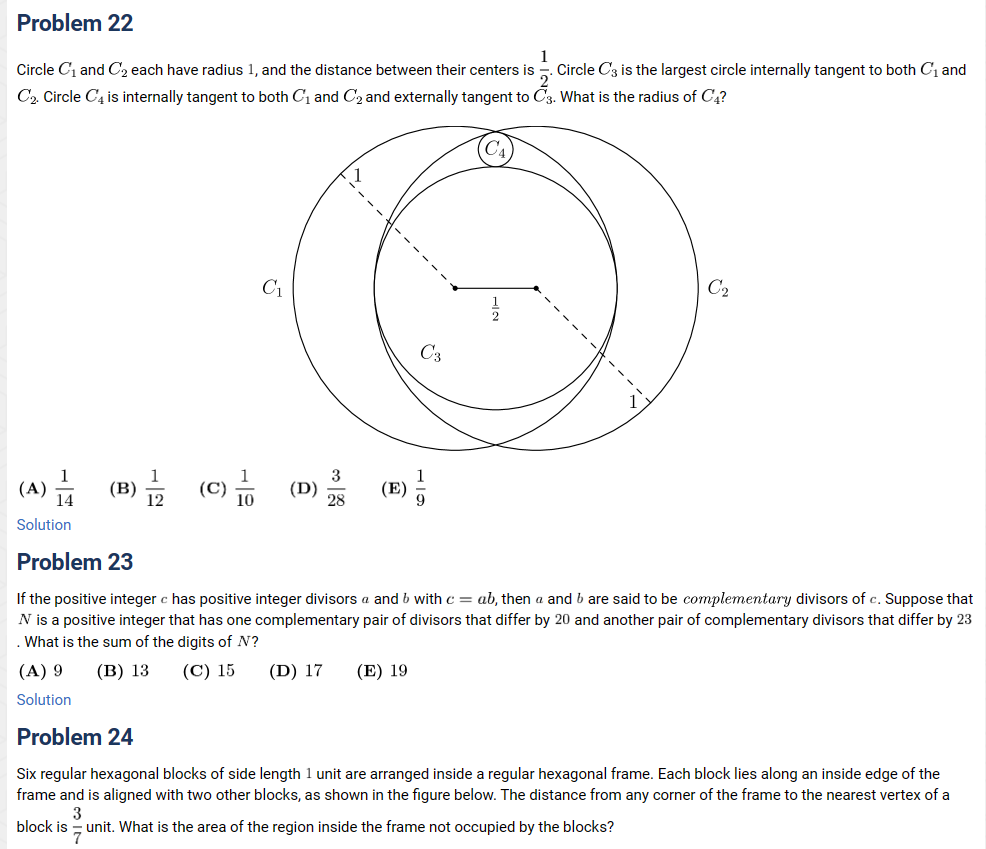
Problem 24
Six regular hexagonal blocks of side length ![]() unit are arranged inside a regular hexagonal frame. Each block lies along an inside edge of the frame and is aligned with two other blocks, as shown in the figure below. The distance from any corner of the frame to the nearest vertex of a block is
unit are arranged inside a regular hexagonal frame. Each block lies along an inside edge of the frame and is aligned with two other blocks, as shown in the figure below. The distance from any corner of the frame to the nearest vertex of a block is ![]() unit. What is the area of the region inside the frame not occupied by the blocks?
unit. What is the area of the region inside the frame not occupied by the blocks?![[asy] unitsize(1cm); draw(scale(3)*polygon(6)); filldraw(shift(dir(0)*2+dir(120)*0.4)*polygon(6), lightgray); filldraw(shift(dir(60)*2+dir(180)*0.4)*polygon(6), lightgray); filldraw(shift(dir(120)*2+dir(240)*0.4)*polygon(6), lightgray); filldraw(shift(dir(180)*2+dir(300)*0.4)*polygon(6), lightgray); filldraw(shift(dir(240)*2+dir(360)*0.4)*polygon(6), lightgray); filldraw(shift(dir(300)*2+dir(420)*0.4)*polygon(6), lightgray); [/asy]](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/c/9/9/c998151e86bba8508b21392100fe7ec037aefa77.png)
![]()
Problem 25
If ![]() and
and ![]() are vertices of a polyhedron, define the distance
are vertices of a polyhedron, define the distance ![]() to be the minimum number of edges of the polyhedron one must traverse in order to connect
to be the minimum number of edges of the polyhedron one must traverse in order to connect ![]() and
and ![]() . For example,
. For example, ![]() is an edge of the polyhedron, then
is an edge of the polyhedron, then ![]() , but if
, but if ![]() and
and ![]() are edges and
are edges and ![]() is not an edge, then
is not an edge, then ![]() . Let
. Let ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() be randomly chosen distinct vertices of a regular icosahedron (regular polyhedron made up of 20 equilateral triangles). What is the probability that
be randomly chosen distinct vertices of a regular icosahedron (regular polyhedron made up of 20 equilateral triangles). What is the probability that 

AMC10B Problem 1
Mrs. Jones is pouring orange juice into four identical glasses for her four sons. She fills the first three glasses completely but runs out of juice when the fourth glass is only ![]() full. What fraction of a glass must Mrs. Jones pour from each of the first three glasses into the fourth glass so that all four glasses will have the same amount of juice?
full. What fraction of a glass must Mrs. Jones pour from each of the first three glasses into the fourth glass so that all four glasses will have the same amount of juice?

Problem 2
Carlos went to a sports store to buy running shoes. Running shoes were on sale, with prices reduced by ![]() on every pair of shoes. Carlos also knew that he had to pay a
on every pair of shoes. Carlos also knew that he had to pay a ![]() sales tax on the discounted price. He had
sales tax on the discounted price. He had ![]() dollars. What is the original (before discount) price of the most expensive shoes he could afford to buy?
dollars. What is the original (before discount) price of the most expensive shoes he could afford to buy?

Problem 3
A ![]() right triangle is inscribed in circle
right triangle is inscribed in circle ![]() , and a
, and a ![]() right triangle is inscribed in circle
right triangle is inscribed in circle ![]() . What is the ratio of the area of circle
. What is the ratio of the area of circle ![]() to the area of circle
to the area of circle ![]() ?
?

Problem 4
Jackson’s paintbrush makes a narrow strip with a width of 6.5 millimeters. Jackson has enough paint to make a strip 25 meters long. How many square centimeters of paper could Jackson cover with paint?

Problem 5
Maddy and Lara see a list of numbers written on a blackboard. Maddy adds ![]() to each number in the list and finds that the sum of her new numbers is
to each number in the list and finds that the sum of her new numbers is ![]() . Lara multiplies each number in the list by
. Lara multiplies each number in the list by ![]() and finds that the sum of her new numbers is also
and finds that the sum of her new numbers is also ![]() . How many numbers are written on the blackboard?
. How many numbers are written on the blackboard?

Problem 6
Let ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() for
for ![]() . How many terms in the sequence
. How many terms in the sequence ![]() are even?
are even?

Problem 7
Square ABCD is rotated 20 degrees clockwise about its center to obtain square EFGH, as shown below. What is the degree measure of ![]() ?
?


Problem 8
What is the units digit of ![]() ?
?

Problem 9
The numbers 16 and 25 are a pair of consecutive postive squares whose difference is 9. How many pairs of consecutive positive perfect squares have a difference of less than or equal to 2023?

Problem 10
You are playing a game. A ![]()
![]()
![]() rectangle covers two adjacent squares (oriented either horizontally or vertically) of a
rectangle covers two adjacent squares (oriented either horizontally or vertically) of a ![]()
![]()
![]() grid of squares, but you are not told which two squares are covered. Your goal is to find at least one square that is covered by the rectangle. A “turn” consists of you guessing a square, after which you are told whether that square is covered by the hidden rectangle. What is the minimum number of turns you need to ensure that at least one of your guessed squares is covered by the rectangle?
grid of squares, but you are not told which two squares are covered. Your goal is to find at least one square that is covered by the rectangle. A “turn” consists of you guessing a square, after which you are told whether that square is covered by the hidden rectangle. What is the minimum number of turns you need to ensure that at least one of your guessed squares is covered by the rectangle?

Problem 11
Suzanne went to the bank and withdrew 800 dollars. The teller gave her this amount using 20 dollar bills, 50 dollar bills, and 100 dollar bills, with at least one of each denomination. How many different collections of bills could Suzanne have received?

Problem 12
When the roots of the polynomial

are removed from the number line, what remains is the union of 11 disjoint open intervals. On how many of these intervals is ![]() positive?
positive?

Problem 13
What is the area of the region in the coordinate plane defined by
![]() ?
?

Problem 14
How many ordered pairs of integers ![]() satisfy the equation
satisfy the equation ![]() ?
?

Problem 15
What is the least positive integer ![]() such that
such that ![]() is a perfect square?
is a perfect square?

Problem 16
Define an ![]() to be a positive integer of 2 or more digits where the digits are strictly increasing moving left to right. Similarly, define a
to be a positive integer of 2 or more digits where the digits are strictly increasing moving left to right. Similarly, define a ![]() to be a positive integer of 2 or more digits where the digits are strictly decreasing moving left to right. For instance, the number 258 is an upno and 8620 is a downno. Let ? equal the total number of
to be a positive integer of 2 or more digits where the digits are strictly decreasing moving left to right. For instance, the number 258 is an upno and 8620 is a downno. Let ? equal the total number of ![]() and let ? equal the total number of
and let ? equal the total number of ![]() . What is |? − ?|?
. What is |? − ?|?

Problem 17
A rectangular box ? has distinct edge lengths ?, ?, and ?. The sum of the lengths of all 12 edges of ? is 13, the sum of the areas of all 6 faces of ? is ![]() , and the volume of ? is
, and the volume of ? is ![]() . What is the length of the longest interior diagonal connecting two vertices of ? ?
. What is the length of the longest interior diagonal connecting two vertices of ? ?

Problem 18
Suppose ?, ?, and ? are positive integers such that ![]() .
.
Which of the following statements are necessarily true?
I. If ![]() or
or ![]() or both, then
or both, then ![]() .
.
II. If ![]() , then
, then ![]() or
or ![]() or both.
or both.
III. ![]() if and only if
if and only if ![]() .
.

Problem 19
Sonya the frog chooses a point uniformly at random lying within the square ![]()
![]()
![]() in the coordinate plane and hops to that point. She then randomly chooses a distance uniformly at random from
in the coordinate plane and hops to that point. She then randomly chooses a distance uniformly at random from ![]() and a direction uniformly at random from {north, south, east, west}. All he choices are independent. She now hops the distance in the chosen direction. What is the probability that she lands outside the square?
and a direction uniformly at random from {north, south, east, west}. All he choices are independent. She now hops the distance in the chosen direction. What is the probability that she lands outside the square?

Problem 20
Four congruent semicircles are drawn on the surface of a sphere with radius 2, as shown, creating a close curve that divides the surface into two congruent regions. The length of the curve is ![]() . What is ??
. What is ??


Problem 21
Each of 2023 balls is randomly placed into one of 3 bins. Which of the following is closest to the probability that each of the bins will contain an odd number of balls?

Problem 22
How many distinct values of ? satisfy ![]() where
where ![]() denotes the largest integer less than or equal to ??
denotes the largest integer less than or equal to ??

Problem 23
An arithmetic sequence of positive integers has ![]() terms, initial term
terms, initial term ![]() , and common difference
, and common difference 1$” width=”41″ height=”13″>. Carl wrote down all the terms in this sequence correctly except for one term, which was off by
![]() . The sum of the terms he wrote down was
. The sum of the terms he wrote down was ![]() . What is
. What is ![]() ?
?

Problem 24
What is the perimeter of the boundary of the region consisting of all points which can be expressed as ![]() with
with ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() ?
?

Problem 25
A regular pentagon with area ![]() is printed on paper and cut out. All five vertices are folded to the center of the pentagon, creating a smaller pentagon. What is the area of the new pentagon?
is printed on paper and cut out. All five vertices are folded to the center of the pentagon, creating a smaller pentagon. What is the area of the new pentagon?

- C
- B
- D
- B
- E
- B
- B
- A
- B
- C
- B
- C
- B
- C
- C
- E
- D
- E
- B
- A
- E
- B
- B
- E
- B
AMC10/12B卷 1-4题相同
AMC12 Problem 1
Mrs. Jones is pouring orange juice into four identical glasses for her four sons. She fills the first three glasses completely but runs out of juice when the fourth glass is only ![]() full. What fraction of a glass must Mrs. Jones pour from each of the first three glasses into the fourth glass so that all four glasses will have the same amount of juice?
full. What fraction of a glass must Mrs. Jones pour from each of the first three glasses into the fourth glass so that all four glasses will have the same amount of juice?

Problem 2
Carlos went to a sports store to buy running shoes. Running shoes were on sale, with prices reduced by ![]() on every pair of shoes. Carlos also knew that he had to pay a
on every pair of shoes. Carlos also knew that he had to pay a ![]() sales tax on the discounted price. He had
sales tax on the discounted price. He had ![]() dollars. What is the original (before discount) price of the most expensive shoes he could afford to buy?
dollars. What is the original (before discount) price of the most expensive shoes he could afford to buy?

Problem 3
A ![]() right triangle is inscribed in circle
right triangle is inscribed in circle ![]() , and a
, and a ![]() right triangle is inscribed in circle
right triangle is inscribed in circle ![]() . What is the ratio of the area of circle
. What is the ratio of the area of circle ![]() to the area of circle
to the area of circle ![]() ?
?

Problem 4
Jackson’s paintbrush makes a narrow strip with a width of 6.5 millimeters. Jackson has enough paint to make a strip 25 meters long. How many square centimeters of paper could Jackson cover with paint?

Problem 5
You are playing a game. A ![]() rectangle covers two adjacent squares (oriented either horizontally or vertically) of a
rectangle covers two adjacent squares (oriented either horizontally or vertically) of a ![]() grid of squares, but you are not told which two squares are covered. Your goal is to find at least one square that is covered by the rectangle. A “turn” consists of you guessing a square, after which you are told whether that square is covered by the hidden rectangle. What is the minimum number of turns you need to ensue that at least one of your guessed squares is covered by the rectangle?
grid of squares, but you are not told which two squares are covered. Your goal is to find at least one square that is covered by the rectangle. A “turn” consists of you guessing a square, after which you are told whether that square is covered by the hidden rectangle. What is the minimum number of turns you need to ensue that at least one of your guessed squares is covered by the rectangle?

Problem 6
When the roots of the polynomial.

are removed from the number line, what remains is the union of 11 disjoint open intervals. On how many of these intervals is ![]() positive?
positive?

Problem 7
For how many integers ![]() does the expression
does the expression![\[\sqrt{\frac{\log (n^2) - (\log n)^2}{\log n - 3}}\]](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/d/c/b/dcb19417f3c2ddfd1ca85657b18676af13834b8a.png) represent a real number, where log denotes the base
represent a real number, where log denotes the base ![]() logarithm?
logarithm?

Problem 8
How many nonempty subsets ![]() of
of ![]() have the property that the number of elements in
have the property that the number of elements in ![]() is equal to the least element of
is equal to the least element of ![]() ? For example,
? For example, ![]() satisfies the condition.
satisfies the condition.

Problem 9
What is the area of the region in the coordinate plane defined by


Problem 10
In the ![]() -plane, a circle of radius
-plane, a circle of radius ![]() with center on the positive
with center on the positive ![]() -axis is tangent to the
-axis is tangent to the ![]() -axis at the origin, and a circle with radius
-axis at the origin, and a circle with radius ![]() with center on the positive
with center on the positive ![]() -axis is tangent to the
-axis is tangent to the ![]() -axis at the origin. What is the slope of the line passing through the two points at which these circles intersect?
-axis at the origin. What is the slope of the line passing through the two points at which these circles intersect?

Problem 11
What is the maximum area of an isosceles trapezoid that has legs of length ![]() and one base twice as long as the other?
and one base twice as long as the other?

Problem 12
For complex numbers ![]() and
and ![]() , define the binary operation
, define the binary operation ![]() by
by![]() Suppose
Suppose ![]() is a complex number such that
is a complex number such that ![]() . What is
. What is ![]() ?
?

Problem 13
A rectangular box ![]() has distinct edge lengths
has distinct edge lengths ![]() and
and ![]() . The sum of the lengths of all
. The sum of the lengths of all ![]() edges of
edges of ![]() is
is ![]() , the sum of the areas of all
, the sum of the areas of all ![]() faces of
faces of ![]() is
is ![]() , and the volume of
, and the volume of ![]() is
is ![]() . What is the length of the longest interior diagonal connecting two vertices of
. What is the length of the longest interior diagonal connecting two vertices of ![]() ?
?

Problem 14
For how many ordered pairs ![]() of integers does the polynomial
of integers does the polynomial ![]() have
have ![]() distinct integer roots?
distinct integer roots?

Problem 15
Suppose ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() are positive integers such that
are positive integers such that![]() Which of the following statements are necessarily true?
Which of the following statements are necessarily true?
I. If ![]() or
or ![]() or both, then
or both, then ![]() .
.
II. If ![]() , then
, then ![]() or
or ![]() or both.
or both.
III. ![]() if and only if
if and only if ![]() .
.

Problem 16
In Coinland, there are three types of coins, each worth ![]() and
and ![]() What is the sum of the digits of the maximum amount of money that is impossible to have?
What is the sum of the digits of the maximum amount of money that is impossible to have?

Problem 17
Triangle ABC has side lengths in arithmetic progression, and the smallest side has length ![]() If the triangle has an angle of
If the triangle has an angle of ![]() what is the area of
what is the area of ![]() ?
?

Problem 18
Last academic year Yolanda and Zelda took different courses that did not necessarily administer the same number of quizzes during each of the two semesters. Yolanda’s average on all the quizzes she took during the first semester was 3 points higher than Zelda’s average on all the quizzes she took during the first semester. Yolanda’s average on all the quizzes she took during the second semester was 18 points higher than her average for the first semester and was again 3 points higher than Zelda’s average on all the quizzes Zelda took during her second semester. Which one of the following statements cannot possibly be true?
![]() Yolanda’s quiz average for the academic year was 22 points higher than Zelda’s.
Yolanda’s quiz average for the academic year was 22 points higher than Zelda’s.
![]() Zelda’s quiz average for the academic year was higher than Yolanda’s.
Zelda’s quiz average for the academic year was higher than Yolanda’s.
![]() Yolanda’s quiz average for the academic year was 3 points higher than Zelda’s.
Yolanda’s quiz average for the academic year was 3 points higher than Zelda’s.
![]() Zelda’s quiz average for the academic year equaled Yolanda’s.
Zelda’s quiz average for the academic year equaled Yolanda’s.
![]() If Zelda had scored 3 points higher on each quiz she took, then she would have had the same average for the academic year as Yolanda.
If Zelda had scored 3 points higher on each quiz she took, then she would have had the same average for the academic year as Yolanda.
Problem 19
Each of ![]() balls is placed in on of
balls is placed in on of ![]() bins. Which of the following is closest to the probability that each of the bins will contain an odd number of balls?
bins. Which of the following is closest to the probability that each of the bins will contain an odd number of balls?

Problem 20
Cyrus the frog jumps 2 units in a direction, then 2 more in another direction. What is the probability that he lands less than 1 unit away from his starting position?

Problem 21
A lampshade is made in the form of the lateral surface of the frustum of a right circular cone. The height of the frustum is ![]() inches, its top diameter is
inches, its top diameter is ![]() inches, and its bottom diameter is
inches, and its bottom diameter is ![]() inches. A bug is at the bottom of the lampshade and there is a glob of honey on the top edge of the lampshade at the spot farthest from the bug. The bug wants to crawl to the honey, but it must stay on the surface of the lampshade. What is the length in inches of its shortest path to the honey?
inches. A bug is at the bottom of the lampshade and there is a glob of honey on the top edge of the lampshade at the spot farthest from the bug. The bug wants to crawl to the honey, but it must stay on the surface of the lampshade. What is the length in inches of its shortest path to the honey?

Problem 22
A real-valued function ![]() has the property that for all real numbers
has the property that for all real numbers ![]() and
and ![]()
![]() Which one of the following cannot be the value of
Which one of the following cannot be the value of ![]()

Problem 23
When ![]() standard six-sided dice are rolled, the product of the numbers rolled can be any of
standard six-sided dice are rolled, the product of the numbers rolled can be any of ![]() possible values. What is
possible values. What is ![]() ?
?

Problem 24
Suppose that ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() are positive integers satisfying all of the following relations.
are positive integers satisfying all of the following relations.
![\[abcd=2^6\cdot 3^9\cdot 5^7\]](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/2/9/e/29e86e43b8f649b005defff6a2fad55137f1f63c.png)
![\[\text{lcm}(a,b)=2^3\cdot 3^2\cdot 5^3\]](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/9/6/e/96e948a17f61e59d4b8d3a22eb5fb3ae138313e4.png)
![\[\text{lcm}(a,c)=2^3\cdot 3^3\cdot 5^3\]](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/d/8/9/d894077385e2b22f41c6d1e8cc018dae3b148cae.png)
![\[\text{lcm}(a,d)=2^3\cdot 3^3\cdot 5^3\]](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/5/6/d/56df1c066d690462e5674b637bcb874a62b53721.png)
![\[\text{lcm}(b,c)=2^1\cdot 3^3\cdot 5^2\]](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/1/0/4/104e9a748bef440670593f6a39cd7c7ad329ca90.png)
![\[\text{lcm}(b,d)=2^2\cdot 3^3\cdot 5^2\]](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/8/d/7/8d7e6c3cd5cfc60253742c496aa5d3610ec049a9.png)
![\[\text{lcm}(c,d)=2^2\cdot 3^3\cdot 5^2\]](https://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/c/8/3/c837d2c0e335f03ada1a0a87f3058689ad6dcebc.png)
What is ![]() ?
?

Problem 25
A regular pentagon with area ![]() is printed on paper and cut out. The five vertices of the pentagon are folded into the center of the pentagon, creating a smaller pentagon. What is the area of the new pentagon?
is printed on paper and cut out. The five vertices of the pentagon are folded into the center of the pentagon, creating a smaller pentagon. What is the area of the new pentagon?

- C
- B
- D
- C
- C
- C
- E
- D
- B
- E
- D
- E
- D
- A
- E
- D
- E
- A
- E
- E
- E
- E
- E
- C
- B
历年真题+测试题大合集超详细
长按图片即可添加客服



